Sewage Treatment
Sewage Treatment
Extended Aeration
Extended Aeration is a type of activated sludge process with no primary settling and very long aerobic detention time to generate less excess sludge overall. It is ideal for smaller flow, modular applications that require low maintenance such as residential subdivisions.
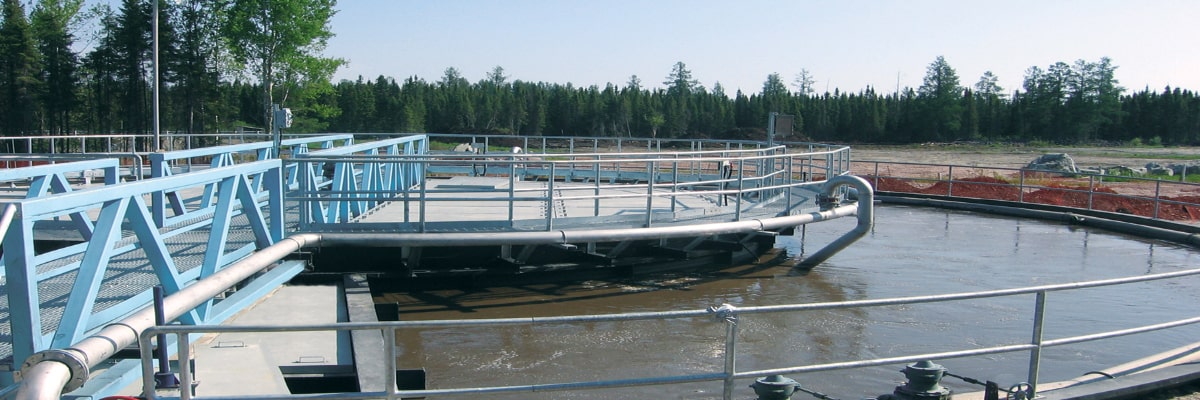

Moving Bed Bio Reactor (MBBR)
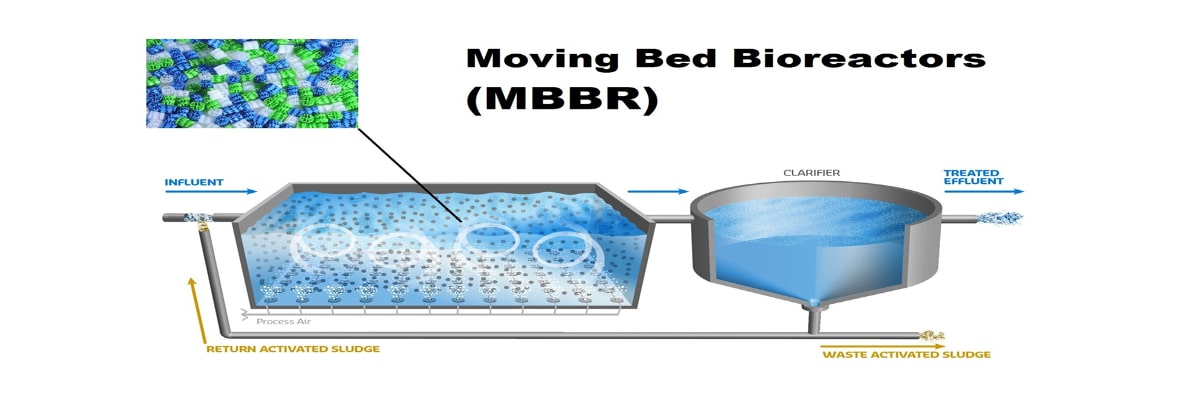
Moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) is a biological technology used for wastewater treatment process suitable for municipal and industrial application. Another common name is moving bed film reactor. It was invented in the 1980s. MBBR offer an economical solution for wastewater treatment. STP MBBR technology is the use of a moving bed biofilm reactor in sewage treatment plants.
MBBR wastewater treatment system enables efficient results of the disposal using low energy. The technology is used to separate organic substances, nitrification and denitrification. MBBR design is made of an activated sludge aeration system. The sludge is collected on the plastic carriers which have a large internal surface area.
The surface area in the carriers optimizes the contact of water, air, and the bacteria. MBBR carriers are cylinders having a cross inside and fins outside to increase the surface area. The standard used is below 70% of carriers in an area of not more than 465m2 per m3. MBBR is used together with a septic tank or a pre-coagulation step for pre-treatment. MBBR technology can be designed with additional non-mechanical or mechanical system to enhance phosphorus and fecal coliform reduction.
Benefits of MBBR Technology
• Saving of space due to its compactness
• Easy to maintain
• Good for a high volume of load
• Extension and expanding are easy. This made possible by increasing the filling degree of carriers.
• Lower discharge costs
• MBBR is not affected by toxic shock
• Independent process performance because there is no return line for sludge; the MBBR eliminates the return activated sludge (RAS)
• It has high effectiveness of sludge retention time (SRT) which enhances the nitrification process
• Production of sludge is lower
• It does not need recycling of the sludge-like activated sludge system
• MBBR media is installed to retrofit existing activated sludge tanks in order to increase its capacity
MBBR technology is effective for wastewater treatment if the regulation concerning the effluent water discharge. The system is flexible in its application and can easily be relocated. Wastewater treatment as required for ecological reasons can be done using the MBBR.
Submerged Aerobic Fixed Film (SAFF)
Submerged Aerobic Fixed Film (SAFF) SAFF Technology incorporates the advantages of Fixed Film Technology combined with Fine bubble Diffused Aeration. SAFF is highly suitable for medium and low strength wastewater. Swaran design good quality submerged aerated filter to reduce the amount of BOD and ammonia nitrogen in settled sewage and industrial effluents.
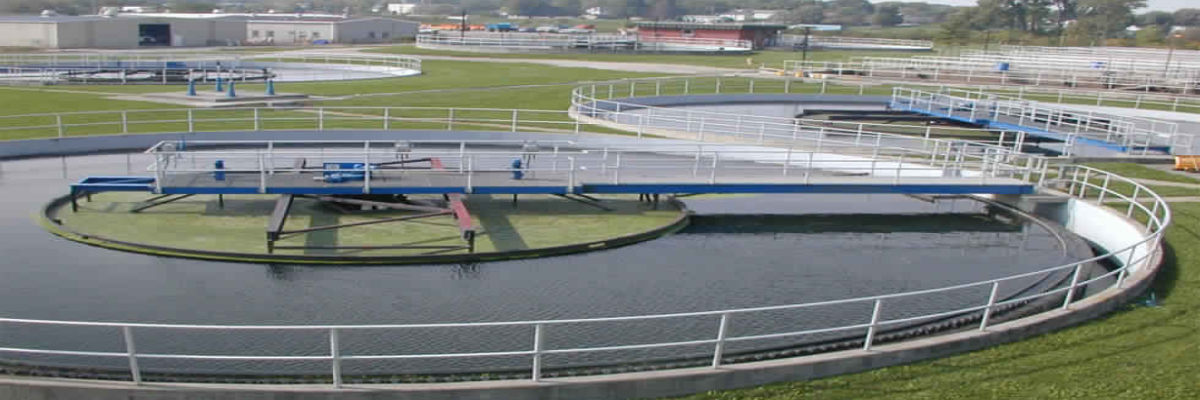

Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR)
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology has emerged as a wastewater treatment technology of choice over the activated sludge process (ASP), which has been the conventional municipal wastewater technology over the last century.
In MBR technology system, the semi-permeable membranes, which are two-dimensional materials, (micro and ultrafiltration) are submerged in aerated biological reactors. This extent of filtration allows the superior quality of sewage to be drawn through the membranes.
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) is a combination of membrane processes like microfiltration or ultrafiltration with a biological wastewater treatment process, the activated sludge process. It is now widely used for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment. A Membrane bioreactor (MBR) processes are mainly used for wastewater treatment (WWT) by using microfiltration (MF) or ultrafiltration (UF) and integrating them with a biological process like a suspended growth bioreactor.
The advantages of MBR systems over conven- tional biological systems include better effluent quality, smaller space requirements, and ease of automation. Specifically, MBRs operate at higher volumetric loading rates which result in lower hydraulic retention times.
The MBR technology provides the following advantages over ASP: High-quality effluent, higher volumetric loading rates, shorter hydraulic retention times (HRT), longer solid retention times (SRT), less sludge production, and potential for simultaneous nitrification/denitrification in long SRTs
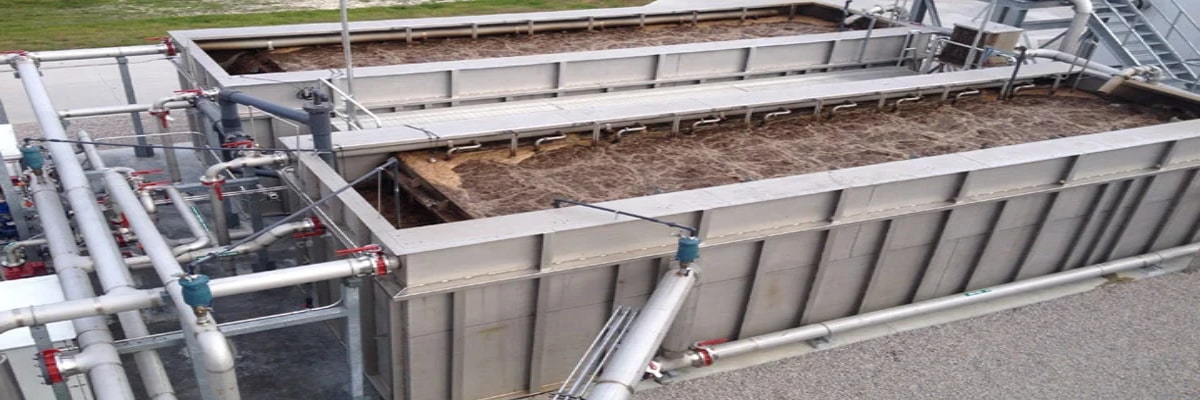

Sequential Batch Reactor (SBR)
The sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a fill-and- draw activated sludge system for wastewater treatment. In this system, wastewater is added to a single “batch” reactor, treated to remove undesirable components, and then discharged.
Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) is an advanced technology that uses a fill and draws activated sludge system for wastewater treatment. It is best for treating both industrial and municipal wastes. The main difference between SBR technology and other STP technologies is that SBR uses a single batch reactor/single tank to process the equalization, aeration, and clarification compared to other technologies that use different batch reactors for various processes.
SBR technology is considered to be one of the highest performed solutions for wastewater treatment. It requires minimum maintenance and has low costs. It can handle continuous batch operations successfully. The distinct qualities of SBR technology are as follows:
• 1. High removal capacity
• 2. Versatile
• 3. Compliant with stringent discharge standards
• 4. High-quality product generation
Here, we know briefly about the SBR technology used in sewage treatment plants (STP) to remove the contaminants from the wastewater. Let us learn about the functioning of SBR technology in STP. One of the most advanced and high-class technology for treating wastewater, it works in various phases in a single batch reactor, often known as tanks. When sewage water is sent to the SBR tanks, then the activated sludge system gets activated. After that, activities occur in a timely sequenced manner, and the water gets purified
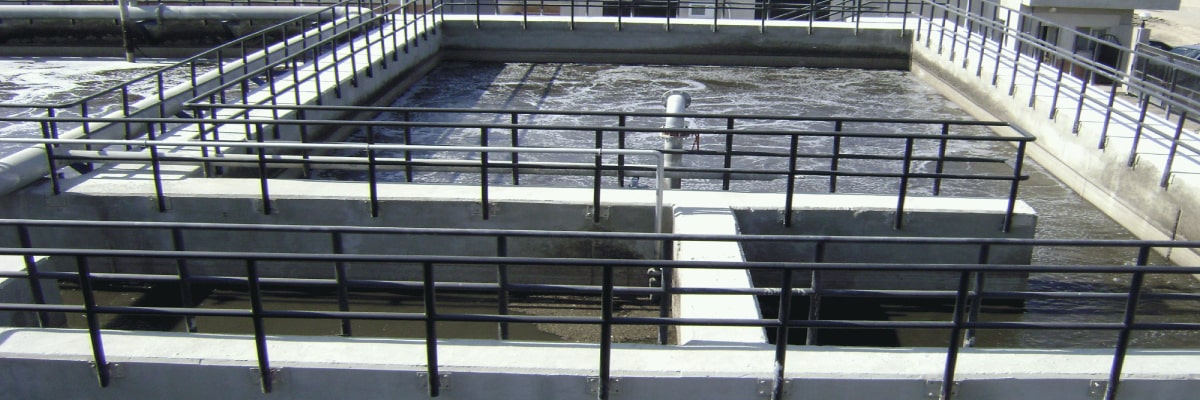

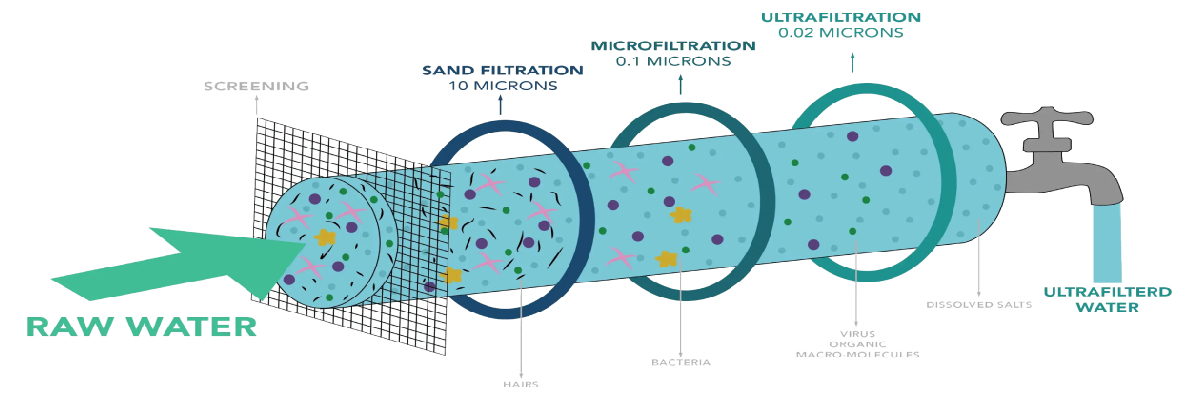
Ultra Filtration
UF or Ultrafiltration technology is used in the water purification system to prevent physical and physical microbial impurities in the water. UF is a type of membrane filtration in which the fluid is compelled to pass through the semipermeable membrane.
It is filtration through a medium (such as a semipermeable capillary wall) which allows small molecules (as of water) to pass but holds back larger ones (as of protein)Ultrafiltration membrane filtration (UF) is a low pressure membrane process for water treatment that is designed to remove turbidity causing particles including those comprised of suspended solids, bacteria, colloidal matter and proteins.
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a pressure-driven purification process that separates particulate matter from soluble compounds using an ultrafine membrane media. Ultrafiltration is an excellent separation technology for desalination pretreatment, reverse osmosis retreatment, and wastewater reclamation, as well as for producing potable water.